Current Status of the Japanese Steel Industry
Previous efforts to reduce CO2 in production processes and issues we are currently facing are explained here.
The blast furnace process is a highly energy-efficient steelmaking process suitable for volume production, but it is considered difficult to achieve carbon-neutral steelmaking through this process because it requires a reducing agent based on a fossil fuel like coke (coal).
In this project, we will study measures to realize carbon-neutral steelmaking that takes advantage not only of the characteristics of blast furnaces but also CCUS technology.
The goal is to implement technology to reduce CO2 emissions by 30% or more from steelmaking processes with technology such as hydrogen reduction technology in blast furnaces using hydrogen from within steelworks and technology to separate and capture CO2 by 2030.
(Assuming CO2 emissions reduction by 10% or more using hydrogen reduction technology and that by 20% or more using separation and capture technology, in total 30% or more.)
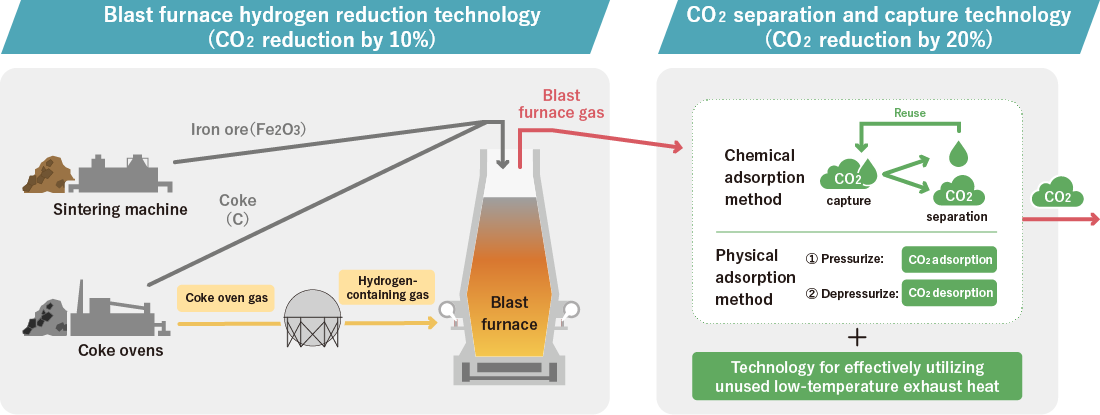
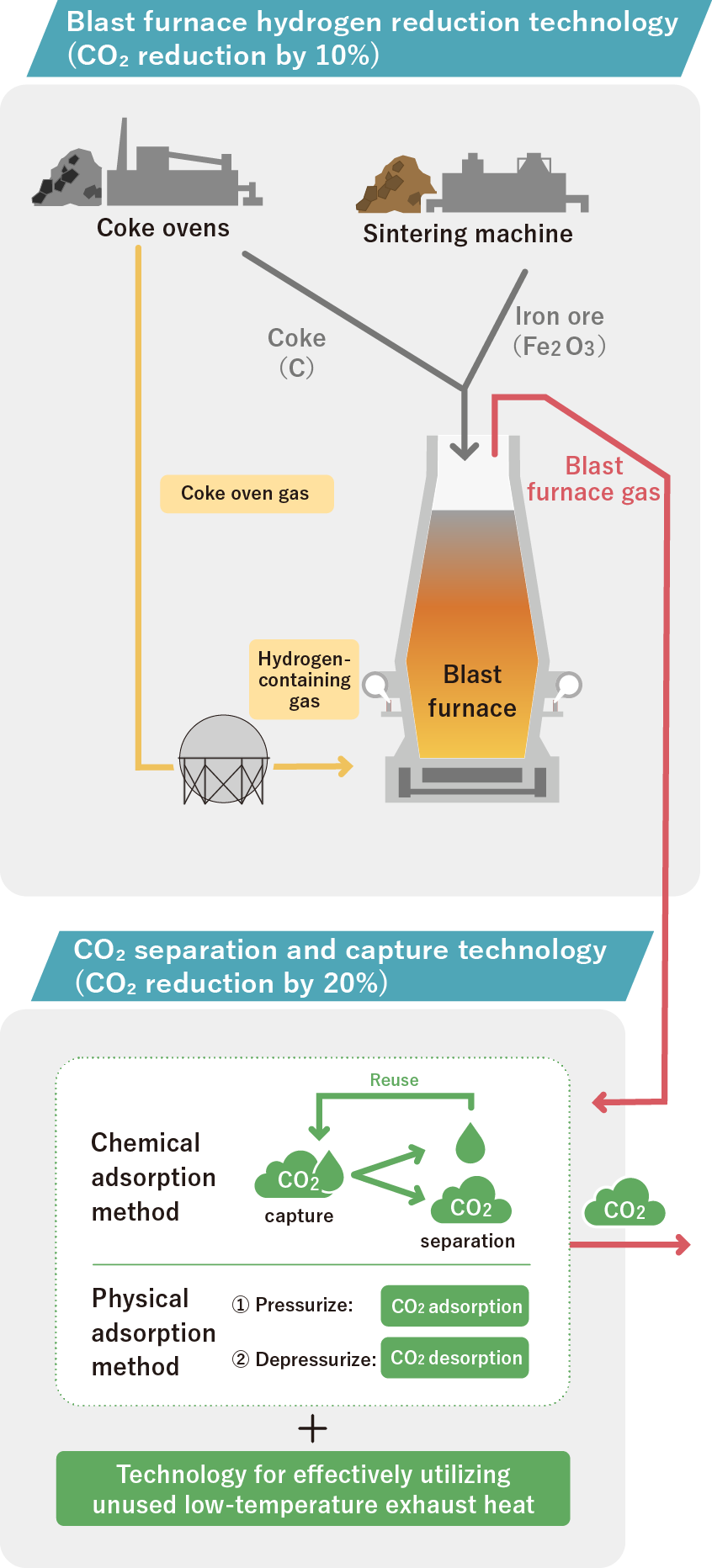
An ambient temperature hydrogen-containing gas injection facility will be introduced in No.2 Blast Furnace at Kimitsu Area, East Nippon Works, Nippon Steel Corporation, and a demonstration test using the actual furnace is scheduled to be started in FY2026.
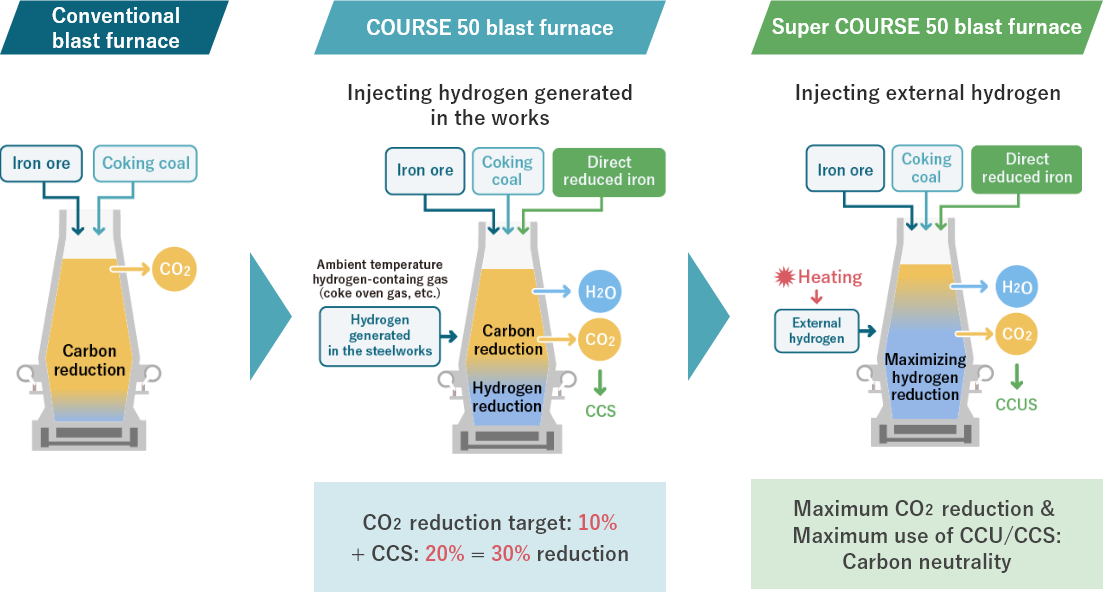
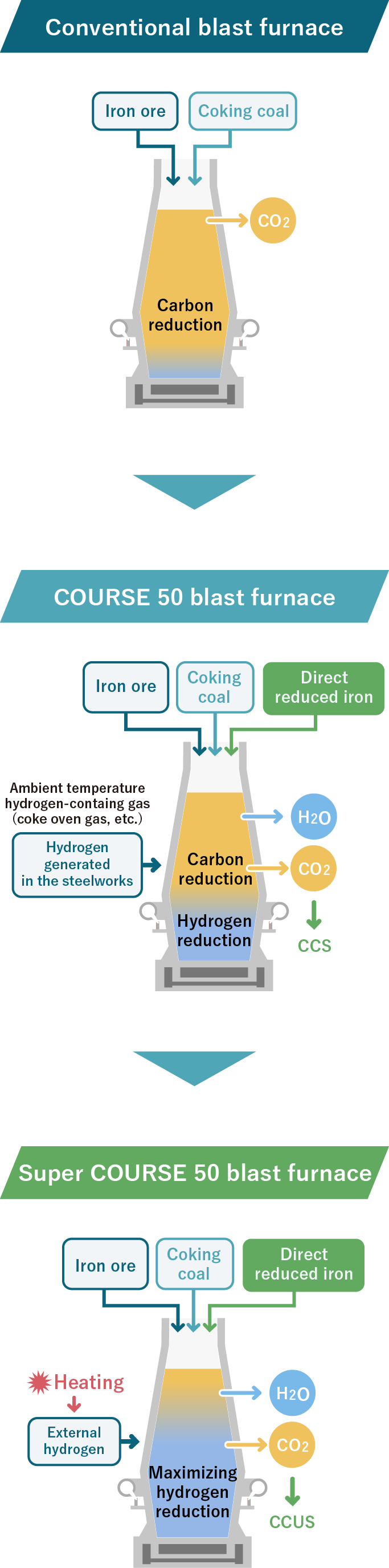
The test blast furnace was remodeled* and a test was started in May 2022 at Kimitsu Area of East Nippon Works, Nippon Steel Corporation.
Part of the coking coal (coke) of the reducing agent was replaced with hydrogen, and part of the iron ore was replaced with direct reduction iron.
Technology to achieve CO2 emissions reduction by 50% or more will be demonstrated compared to the conventional blast furnace process.
* The 12m3 test blast furnace for the COURSE 50 project was used.
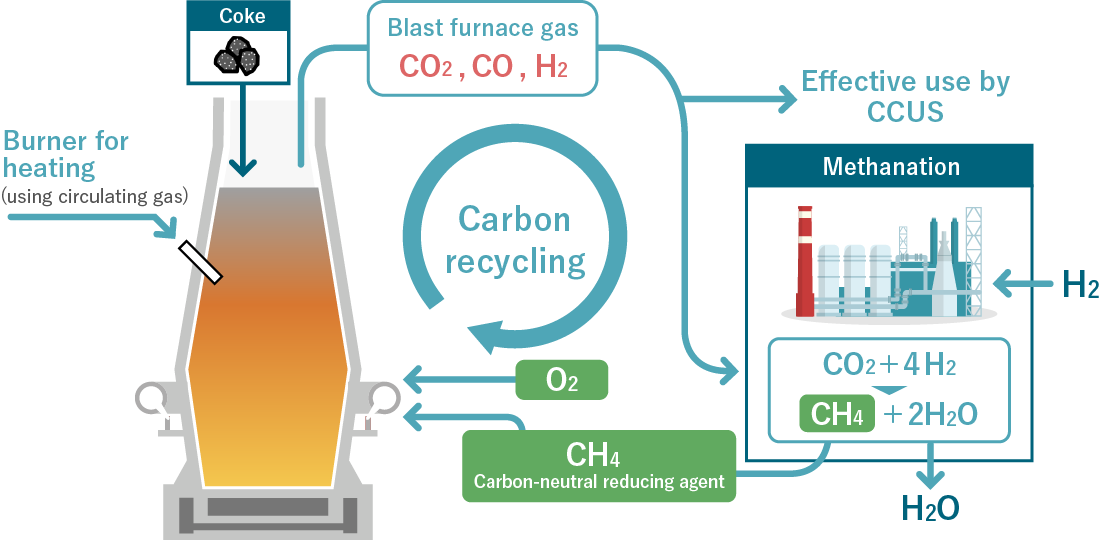
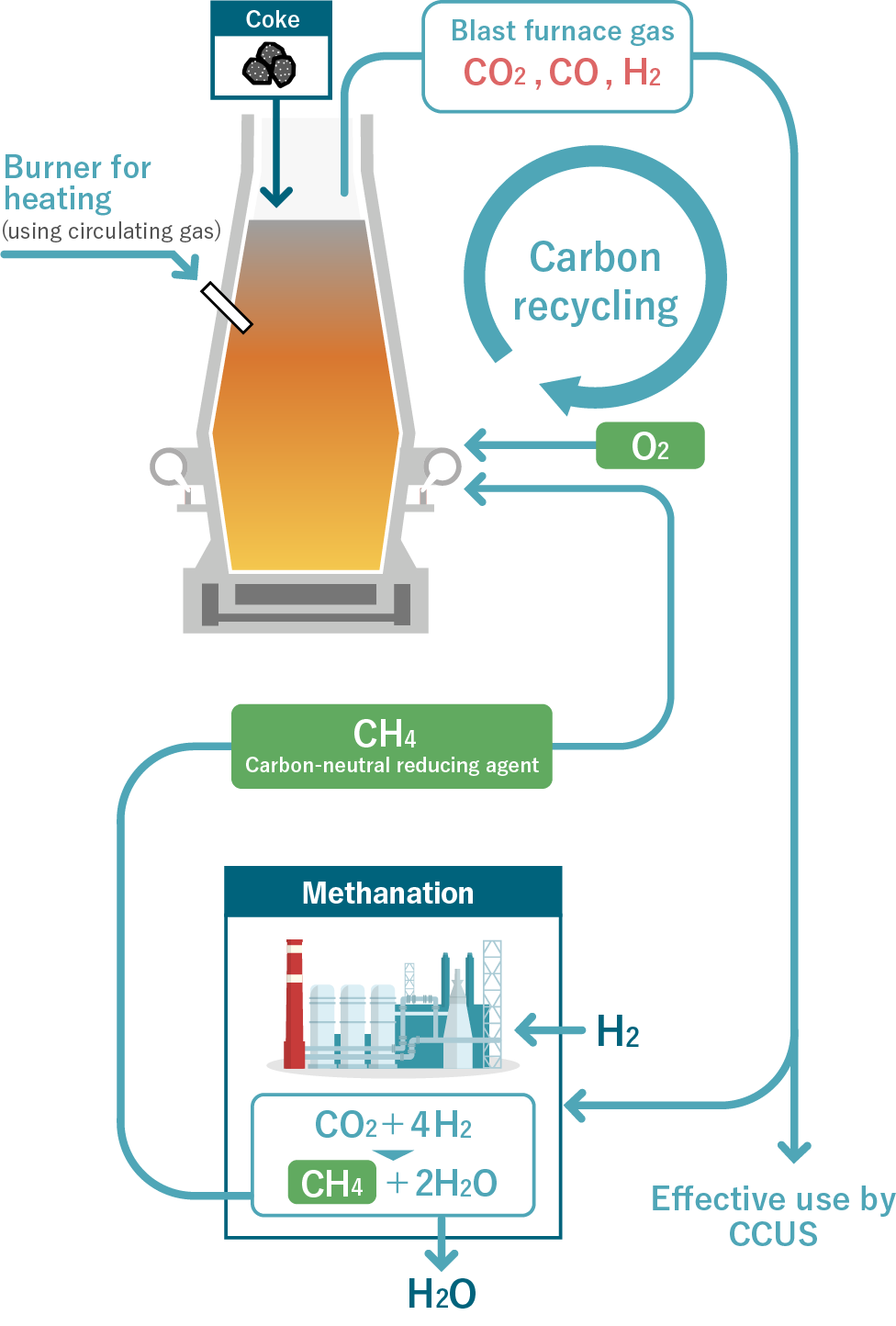
A small-scale carbon-recycling test blast furnace (150 m3) will be constructed at Chiba Area of East Japan Works, JFE Steel Corporation. A test operation will be conducted to check the principles of the process from April 2025 to FY2026.
Technology to achieve CO2 emissions reduction by 50% or more has been demonstrated compared to the conventional blast furnace process.
 01
01Previous efforts to reduce CO2 in production processes and issues we are currently facing are explained here.
 02
02various technological issues to be addressed for realizing steelmaking using hydrogen. We will also address these issues.
 03
03In this project, we will study measures to realize carbon-neutral steelmaking that takes advantage not only of the characteristics of blast furnaces but also CCUS technology.
 04
04In this project, we will study measures to realize direct reduction ironmaking using hydrogen in a shaft furnace.
 05
05In this project, we will work to develop a technology for manufacturing high-grade steel by melting reduced iron manufactured by a direct reduction process.